
- #View vpn dns servers mac command line update
- #View vpn dns servers mac command line full
- #View vpn dns servers mac command line password
Whether to ask peer ppp server for DNS server addresses and let pppd rewrite /etc/nf. This lowers limits on dh key.Īpplies to TLS v1.2 or lower only. If -cipher-list is not specified, add to the list of ciphers.

Use minimum TLS version instead of system default. (default: HIGH:!aNULL:!kRSA:!PSK:!SRP:!MD5:!RC4)Īpplies to TLS v1.2 or lower only, not to be used with TLS v1.3 ciphers. If default does not work, you can try alternatives such as HIGH:!MD5:!RC4 or as suggested by the Cipher: line in the output of openssl(1) (e.g. If your server requires a specific cipher, consider using -cipher-list instead. insecure-sslĭo not disable insecure SSL protocols/ciphers. This option can be used multiple times to trust several certificates. The certificate has to be encoded in DER form. If classical SSL certificate validation fails, the gateway certificate will be matched against this value. Use specified PEM-encoded key if the server requires authentication with a certificate. This feature requires the OpenSSL PKCS engine! -user-key= user-cert = pkcs11:model=PKCS%2315%20emulated manufacturer=piv_II serial=012345678 token=someuser
#View vpn dns servers mac command line full
It takes the full or a partial PKCS11-URI (p11tool -list-token-urls) Use at least the string pkcs11: for using a smartcard. Use specified PEM-encoded certificate if the server requires authentication with a certificate. Use specified PEM-encoded certificate bundle instead of system-wide store to verify the gateway certificate. If it is set to false, the builtin fallback mechanism is used even if resolvconf is available. Set if openfortivpn should use resolvconf to add DNS name servers in /etc/nf.
#View vpn dns servers mac command line update
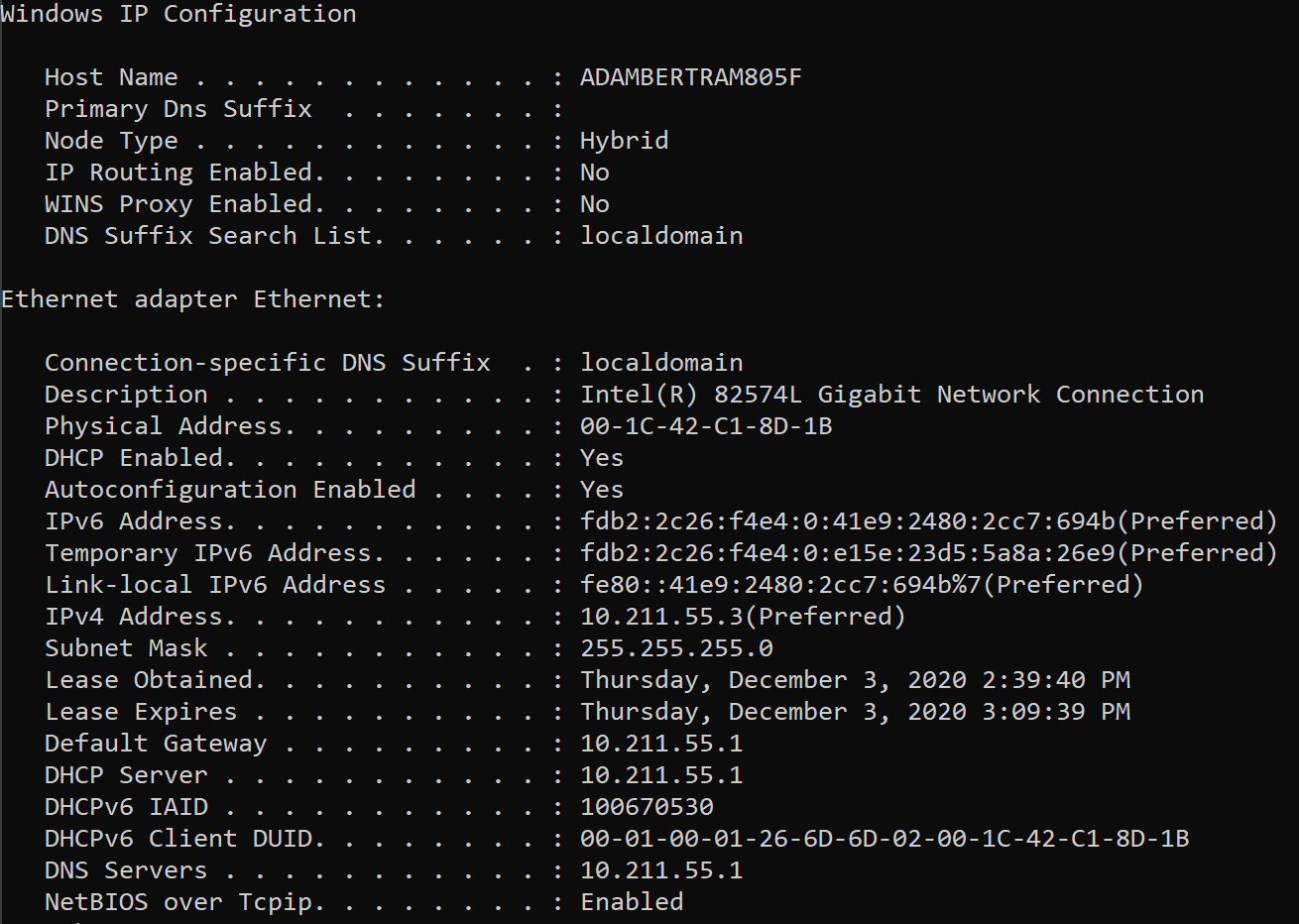
Note that there may be other mechanisms to update /etc/nf, e.g., -pppd-use-peerdns in conjunction with an ip-up-script, which may require that openfortivpn is called with -no-dns. resolvconf is instructed to do the update of the nf file if it is installed and -use-resolvconf is activated, otherwise openfortivpn prepends its changes to the existing content of the nf file. Also a dns-suffix may be received from the peer and added to /etc/nf in the turn of adding the name servers. Set if openfortivpn should add DNS name servers in /etc/nf when tunnel is up. Set if openfortivpn should add two 0.0.0.0/1 and 128.0.0.0/1 routes with higher priority instead of replacing the default route. no-routes is the same as -set-routes= 0. If used multiple times, the last one takes priority.
Set if openfortivpn should try to configure IP routes through the VPN when tunnel is up. ifname= īind the connection to the specified network interface. Defaults to empty, which is usually what you want. realm= Ĭonnect to the specified authentication realm. If this option is provided, authentication based on OTP will be used instead. The server may be configured to allow two factor authentication through a push notification to the mobile application. no-ftm-pushĭo not use FTM push if the server provides the option.

The delay time must be specified in seconds, where 0 means no wait (this is the default). Set the amount of time to wait before sending the One-Time-Password.
#View vpn dns servers mac command line password
Search for the OTP password prompt starting with the string. For example: pinentry-gnome3 on Linux, or pinentry-mac on macOS. Allows supplying the password in a secure manner. For a secure alternative, use pinentry or let openfortivpn prompt for the password. Specify a custom configuration file (default: /etc/openfortivpn/config). Openfortivpn connects to a VPN by setting up a tunnel to the gateway at.

Client for PPP+SSL VPN tunnel services Examples (TL DR)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
